 |
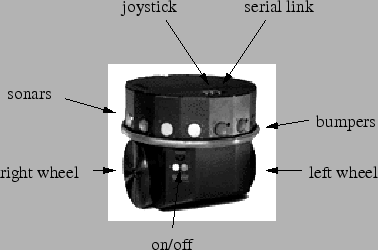
Charm is a Scout robot from Nomadic Technologies Inc [14,22].
Charm is not independent. It has to be controlled by a host computer via a serial link. A Motorola MC68332 main processor is responsible for this communication and a DSP processor is responsible for the motor control. Table 3.2 summarizes its physical characteristics.
Charm is equipped with 16 sonar sensors and 6 independent bumper switches. It has a two wheel differential drive system. The user can provide the speed of each motor independently.
Charm is controlled by a 486 PC running Linux via its serial port. Therefore, the software of the Scout provided by Nomadic Technologies is mostly compatible with the software of the Nomad 200 [21,22]. This allowed us to change the robot during the project and to run the same code with only a few changes in it. The same graphical user interface as FortyTwo's one can be used with Charm.