 |
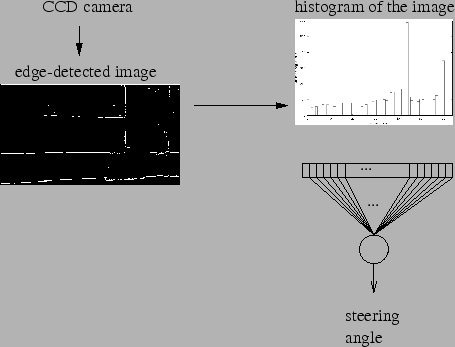
The first experiment was done in the laboratory using a fake corridor made of boxes. The other experiments were in a real corridor. Each image grabbed by the robot is processed as described in figure 3.3.
 |
For all these experiments, the robot was continuously moving forwards using a fixed speed. For each iteration, an image was captured and processed by the robot as described above. The robot then turned its wheels towards the direction computed by the neural network.
Another program was used to capture the position of the robot each time it moved, in order to see how well the robot performed.
The experiment was done in two parts. The first part is the learning part. The experimenter trained the robot with the joystick. In the training stage, the target output was taken from the joystick and the inputs from the processed image. In the testing stage, the inputs of the neural network was taken from the processed image, and the output was computed using the propagation algorithm which is only a weighted sum here.